Introduction to Data Analysis
What is Data Analysis?
The process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the objective of discovering useful information, arriving at conclusions, and supporting the decision making process is called Data Analysis.
Data Analysis and its varieties.
There are multiple facets and approaches with diverse techniques for data analysis. The data analysis in statistics are generally divided into descriptive statistics, exploratory data analisys (EDA), and confirmatory data analysis (CDA). Data need to be cleaned. Data cleaning is the process of correcting the outliers and other incorrect and unwanted information. There are several types of data cleaning proecss to employ depends on the tpe of data to be cleaned. For quantitative data methods the outlier detection can be used to get rid of anomaly in the data. Spellcheckers can be used to lessen the amount of mysteped words in case of textual data.
Business intelligence covers the data analysis that run heavely on aggregation, disaggregation, slicing and dicing, fosusing on the business information. Predictive analytics is the application of statistical or structural models for predictive forecasting. Text analytics is the application of statistical, linguistic, and structural models to extract and classify information from texts.
Steps of Data Analysis:
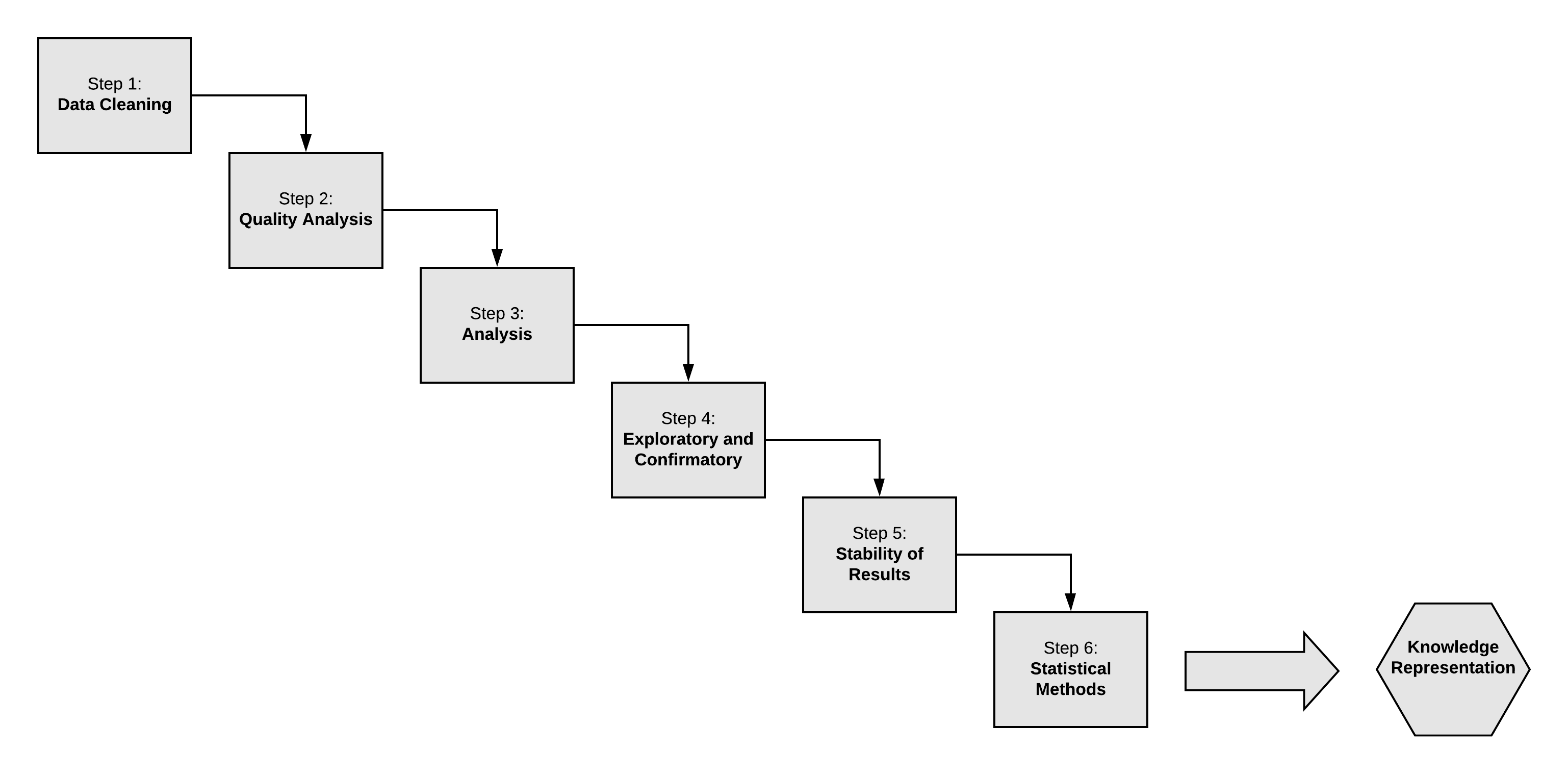
How is Data Analysis Performed?
Data analysis is a part of a larger process of deriving business intelligence. The process includes one or more of the following steps:
- Posing Questions: An attempt is made to ask a question in the problem domain. For example, do red sports cars get into accidents more often than others?
- Data Collection: Data relevant to the question must be collected from the appropriate sources. In the example above, data might be collected from a variety of sources including: DMV or police accident reports, insurance claims and hospitalization details. When data is being collected using surverys, a questionnaire to be presented to the subjects is needed. The questions should be appropriately modeled for the statistical method being used.
- Data Wrangling: Raw data may be collected in several different formats. The collected data must be cleaned and converted so that data analysis tools can import it. For our example, we may receive DMV accident reports as text files, insurance claims from a relational database and hospitalization details as an API. The data analyst must aggregate these different forms of data and convert it into a form suitable for the analysis tools.
- Data Analysis: This is the step where the cleaned and aggregated data is imported into analysis tools. These tools allow you to explore the data, find patterns in it, and ask and answer what-if questions. This is the process by which sense is made of data gathered in research by proper application of statistical methods.
- Drawing Conclusions and Making Predictions: This is the step where, after sufficient analysis, conclusions can drawn from the data and appropriate predictions can be made. These conclusions and predications may then be summarized in a report delivered to end-users.
In the next posts we will take a look in some detail at the methods of data analysis in particular.